Being sexually active means you run the risk of contracting a sexually transmitted disease (STD), also called a sexually transmitted infection (STI). High-risk behaviour, such as having multiple partners or not using a condom, increases your chances of catching an STD or STI, but you should be aware of the different types of sexually transmitted diseases out there and how to protect yourself. Some STDs can be cured, while others cannot, such as HIV and AIDS but even those have treatments available to control them.
First, a little clarification – we will use STI and STD interchangeably in this article because they are essentially describing the same category of infectious diseases. According to some, an STI is an infection that has yet to develop symptoms, while an STD is a full-blown disease exhibiting symptoms. But for our purposes here, they are all sexually transmitted, and they should be of concern.
What is important to remember is that sexually transmitted infections are not things to be ashamed of. They are a fact of life, and the best way to stay healthy is to educate yourself about the different types of STIs and to get tested as soon as possible if you think you have contracted or been exposed to a sexually transmitted disease. This article will provide you with an overview of Sexually Transmitted Diseases in general and descriptions of some of the more common ones.
What Are Sexually Transmitted Diseases?
As their names suggest, sexually transmitted diseases or infections are medical conditions that are usually transmitted by sexual contact. They are caused by bacteria, parasites, or viruses that travel from person to person through semen, vaginal fluids, blood, or other bodily fluids. Since this type of transmission is usually through oral, vaginal, or anal sex, they are called STDs or STIs. However, if infected bodily fluids come into contact with your broken skin, such as through an open cut or sore or a contaminated blade or needle, you may risk catching an Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Furthermore, pregnant mothers who are infected risk passing that STI on to their child during pregnancy or childbirth.
Speaking of symptoms, STIs each have their own set of symptoms, but there are general signs that could mean you have a sexually transmitted disease:
- Itching, sores, or bumps in or around genitals, mouth, or rectum
- Lower abdominal pain
- Rash appearing around genitals, buttocks, or abdomen
- Fever
- Unusual vaginal discharge (smelly, discoloured) or bleeding
- Discharge from penis
- Pain during sex or urination
- Swollen lymph nodes (usually those in the inner upper thigh area
If you or your partner have any of these symptoms, you may want to have an examination or be tested. Nevertheless, we cannot stress enough how STDs can still be passed from person to person even if there are no apparent symptoms. That is why it is so important to get tested if you feel you are at risk. If you are sexually active with multiple partners, it is important to consider having regular screenings, if only for your peace of mind and to assure your partner.
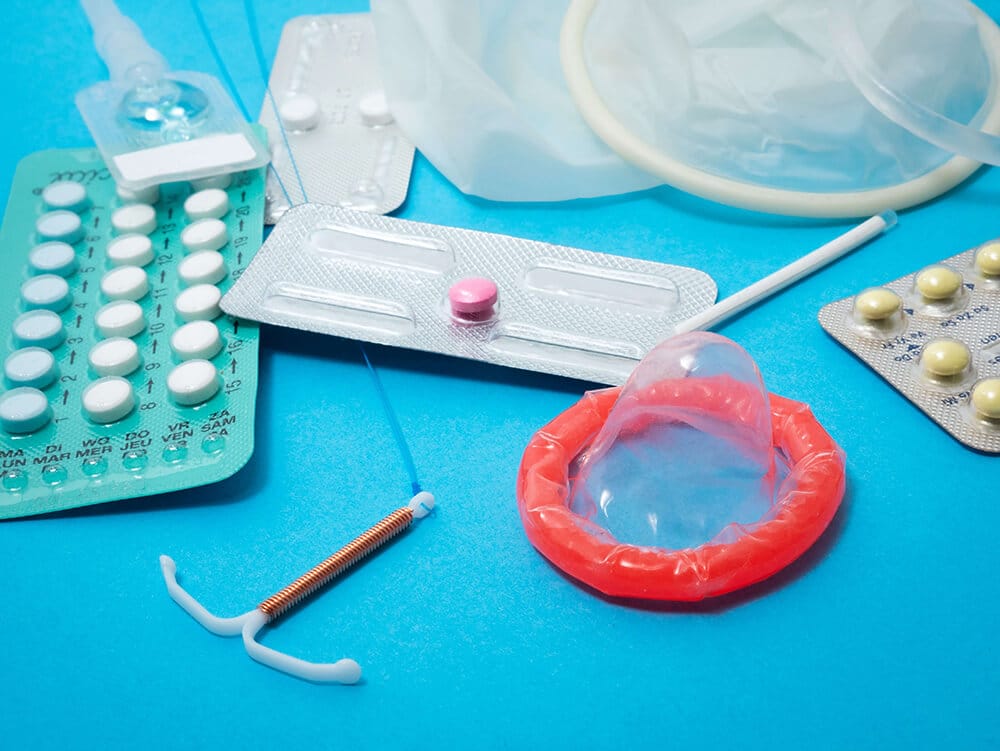
How to Avoid STDs?
Of course, the best way to avoid Sexually Transmitted Diseases or STIs is to avoid sexual contact completely, but that is not necessarily the most reasonable or practical option for many people.
You should discuss STDs with your partner before engaging in any sexual activity. Ideally, you both should be tested as well, but this is not always the case. You should always use protection, such as condoms, dental dams, or latex gloves, during oral, anal, or vaginal sex. This protection, when used properly, will create a barrier to prevent fluid exchange and skin-to-skin contact.
Basic hygiene is also important, so washing thoroughly before and after sex helps lower the chance of contagion for some STDs. This includes keeping any toys clean, too. There are also vaccines available for some STDs. Another consideration is alcohol and drug use. While we do not want to make any moral decrees, it can be said that most people’s judgement is impaired if they are drunk or high, so safe sex may not be at the front of mind while partying. Just some food for thought.
Also, if you have an Sexually Transmitted Diseases or STI, you should always use safe sex practices. For example, if you have symptoms, you should avoid all sexual contact.
All these measures are not completely failproof, but safe sex practices do reduce the risk of contracting Sexually Transmitted Diseases significantly.

Common Sexually Transmitted Diseases
These are among the most common sexually transmitted infections:
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is one of the most common Sexually Transmitted Diseases, most likely because it generally does not show any symptoms. If there are symptoms, it is usually pain or unusual discharge. It is a bacterial infection that is easily cleared up with antibiotics. If left untreated, it could cause long-term, serious problems, including chronic testicular inflammation, pelvic inflammatory disease, and infertility. Because it is typically asymptomatic, most medical professionals urge both men and women to get tested at least once a year or if they have sex with a casual or new partner.
Gonorrhoea
Gonorrhoea is another very common bacterial infection. It also has been called “the clap”. It is very contagious during sexual contact – oral, vaginal, and anal. It tends to infect the cervix, urethra, or rectum, and it could, although rarely, infect the throat or eyes. Left untreated, issues like infertility, chronic pain, and potential sepsis could occur.
Symptoms, for both men and women, include greenish or yellow discharge or urination pain. However, there is a significant chance that you can be infected and not show symptoms, which is why testing is important, as well as notifying partners if you test positive. Luckily, gonorrhoea is easily treated with antibiotics, usually a single injection.
Syphilis
Syphilis is another bacterial infection spread through sexual contact. It was once a deadly infection, causing deaths by the millions, when it was thought that mercury was the only treatment. With the discovery of antibiotics, syphilis was thought to be eradicated. Unfortunately, syphilis infections are apparently on the rise – the Center for Disease Control in the United States marked an over 50% increase in cases between 2016 and 2020.
This could be because syphilis symptoms seem mild – small sores, mild rashes, or flu-like conditions. Also, it takes three weeks for symptoms to appear, and sometimes the symptoms may clear up. This does not mean that the infection is gone. Untreated, syphilis can cause heart problems, dementia or other neurological issues, and a host of other problems.
HIV/AIDs
HIV is a viral infection that can cause AIDS, which can be a terminal illness. HIV is transmitted through bodily fluids, which means sexual contact, but can also include blood transfusions, shared needles (drugs, piercings, tattoos, etc.), or through pregnancy. HIV is usually asymptomatic and can be controlled with anti-viral medicines to prevent it from breaking out into AIDS. Since HIV does not exhibit symptoms, it is essential to be tested if you think you are at risk.
Once HIV develops into AIDS, things can go downhill as AIDS means your immune system is compromised so that you are at high risk of developing dangerous infections. Nevertheless, with proper medication and treatment, if caught in time, people with HIV can live a healthy life for decades.
It is important to be familiar with post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) and pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). If you think you may become exposed to HIV, PrEP can reduce the risk of transmission significantly. If you have already been exposed to HIV, within 72 hours, PEP can reduce the risk of HIV transmission.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that can lead to severe liver damage. Like HIV, it can be contracted through sexual contact, as well as through blood contact. This blood contact is not just with needles, but it has been known to be passed through small amounts of blood in shared toothbrushes and razors. Hepatitis B is highly contagious in those ways, but it cannot be passed through saliva or by sharing food (other forms of hepatitis, such as hepatitis A, can).
Some signs of hepatitis B include fatigue, loss of appetite, jaundice (sallow, yellowish skin or eyes), joint pain, and fever. As with other Sexually Transmitted Diseases, you could have hepatitis B and not show symptoms. Unfortunately, there is no cure for hepatitis B, but there is an effective vaccine. If you do contract this form of hepatitis, you will need to discuss treatment with your doctor to prevent long term issues, such as cirrhosis.
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is caused by a virus, and some people will only develop an acute illness that will clear itself after weeks or months. However, over half of the people infected will have contracted a chronic form of hepatitis C. Like hepatitis B, it is transmitted by bodily fluids that contain blood. Having sexual contact, sharing drug equipment, unsterile tattoo or piercing equipment, needlesticks or sharps can all put you at risk.
You have an elevated risk if you are a male over 50, consume alcohol, or have an existing liver disease. The signs are similar to hepatitis B, but many people exhibit no symptoms. Left untreated, cirrhosis and liver cancers are the major risks. The treatment is effective and in the form of a course of antiviral drugs (for both acute and chronic cases) for 8-10 weeks, which clears hepatitis C in 90% of patients.
Emerging Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Ureaplasma and Mycoplasma Genitalium
These are two types of tiny bacteria that are labelled as emerging STDs. The symptoms, if any, are often confused with other STDs such as bacterial vaginosis (BV) and chlamydia. The bacteria can often lead to urethritis, causing pain during urination, itching, discharges, and odours. These emerging Sexually Transmitted Diseases often do not show symptoms and will not always clear themselves. Therefore, you should be tested for it and treated correctly. If left untreated, you risk infertility, pelvic inflammation disease (PID), and other pregnancy complications.
Other common Sexually Transmitted Diseases
The above is by no means a complete list of STIs. Other sexually transmitted infections include
- Herpes: blisters and sores around mouth or genitals. Treatable but no cure.
- HPV: asymptomatic virus that is incurable and some strains can lead to genital warts or certain cancers.
- Pubic lice (also called “crabs”): parasites attached to skin and hair around genitals. Easily treated and cured.
- Trichomoniasis: parasitic infection that can cause irritation and smells. Easily treated and cured.
And this is still not all.

Bottom line: Visit MedConsult and get tested
Sex should be pleasurable and should not cause fear, but sexually transmitted diseases and infections should be a concern, especially if you do not practice safe sex. Lower your risk for infection by using protection and getting tested. If you are sexually active in a low-risk relationship, then you should get tested at least once a year or if you are experiencing symptoms. If you are entering a new relationship or have had higher risk activity, you should get tested immediately and more often.
Not sure what to do? Do not stay quiet and hope it all goes away. Consult a trusted medical professional for advice, physical examination, or testing. Also, many Sexually Transmitted Diseases can now be diagnosed with self-testing kits. That means that if you feel embarrassed, you can test yourself in the comfort of your own home. Just ask us about these tests. Furthermore, we can organize treatment to be sent to your home as well, so you never even need to step foot in our clinic.
The team at MedConsult is highly trained and very discreet – they are trusted by their patients for their attention to detail and comprehensive care.

MedConsult Clinic
Dr Donna Robinson founded MedConsult Clinic in 2003 to offer high-quality, affordable medical care in Bangkok. With over 35 years of experience, she oversees a team of medical practitioners and nurses who provide healthcare services in English, Thai, Japanese, Chinese, Burmese, and other languages. Dr Donna herself is fully bilingual in English and Thai and holds UK and Thai medical licenses.

